Open six days a week - book a consultation with a specialist now - No Hidden Charges, No Pressure, Affordable
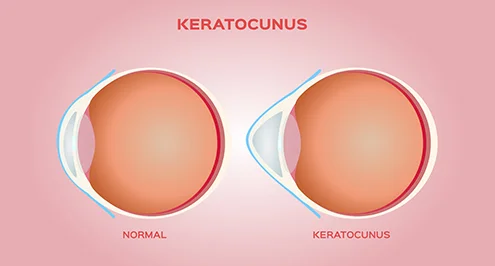
CAIRS (Corneal Allogenic Intrastromal Ring Segments) is a surgical technique used to treat keratoconous, an eye condition where the cornea thins and bulges into a cone shape. This innovative procedure involves implanting custom-designed corneal segments made from donor tissue into the patient's cornea. Unlike INTACS, which use synthetic materials, CAIRS uses biological, donor-derived tissue, making the procedure more biocompatible and potentially offering better healing and integration with the patient's natural cornea.
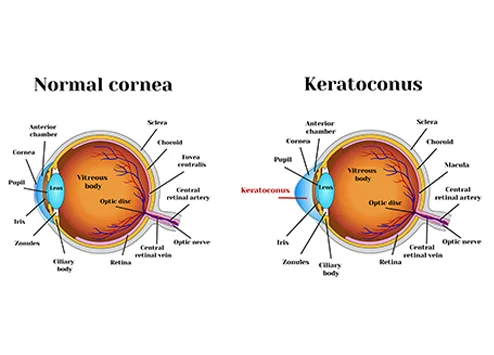
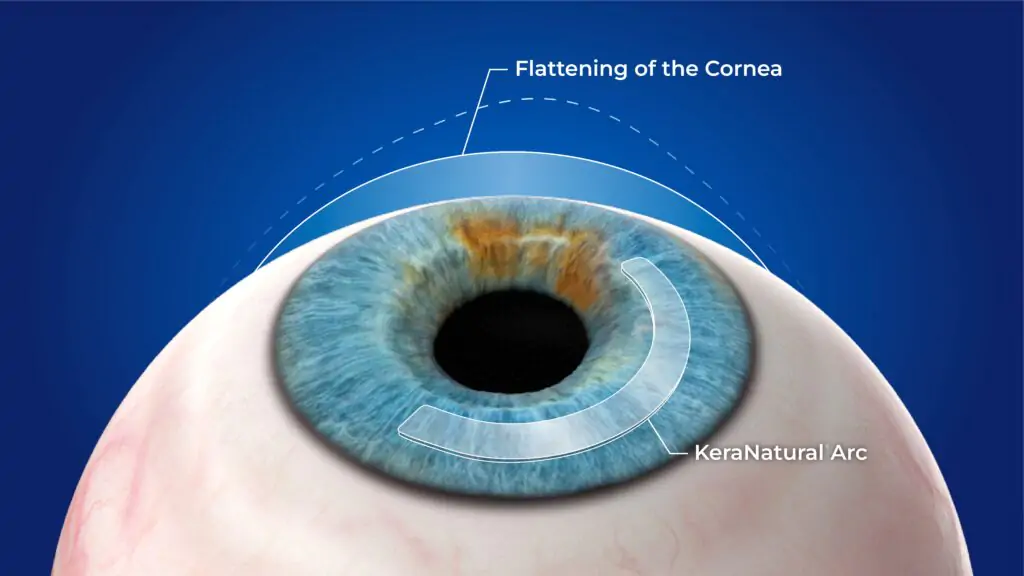
CAIRS is a promising, minimally invasive option for patients with keratoconous, offering a natural and biocompatible way to reshape the cornea and improve vision. By using donor corneal tissue, CAIRS has the potential to reduce complications associated with synthetic implants and provide more natural healing. For patients seeking alternatives to synthetic implants like INTACS, CAIRS may be an excellent option, particularly when combined with other treatments like corneal cross-linking to halt the progression of keratoconous.

Dr Mani has performed more than 35,000 ophthalmic procedures, including LASIK, LASEK, PRK, Femto Cataract, RLE, Lens ICL and Phakic IOL Surgery

We are recognised by most UK and international medical insurance providers.
Please call us to ask about private healthcare insurance.







